Introduction:
In today’s digitally connected world, a reliable and high-performing network is crucial for smooth communication and data transfer. One essential aspect of network performance assessment is the measurement of jitter. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of jitter, its impact on network quality, and how Jitter Test can help diagnose and optimize network performance. Whether you’re an IT professional or simply interested in learning more about network metrics, this article will provide you with valuable insights.
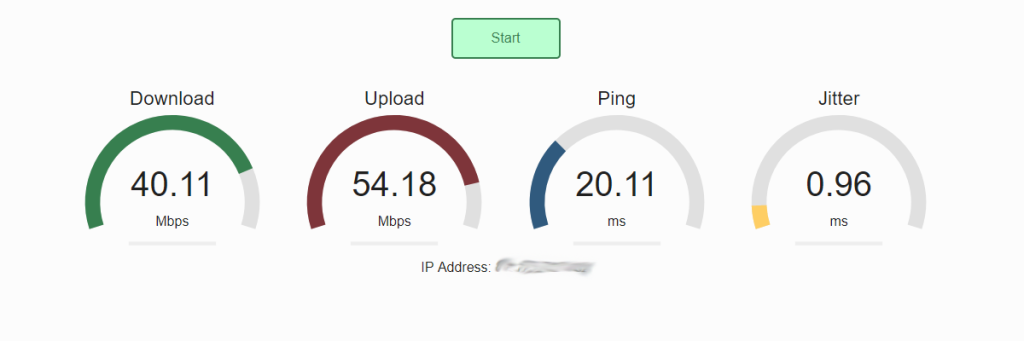
What is Jitter
Jitter refers to the variation in the delay of packet arrival within a network. It is often caused by inconsistencies in the transmission of data packets. When data is transmitted, it is divided into smaller packets that travel across the network individually before being reassembled at the destination. Ideally, these packets should arrive at regular intervals, ensuring smooth data delivery.
However, due to network congestion, hardware limitations, or other factors, the packets can experience delays or arrive out of order. Jitter measures the difference in packet arrival times, indicating the level of inconsistency or instability in the network’s performance.
The Impact of Jitter on Network Quality.
Jitter can have a significant impact on network quality, affecting various aspects of communication and data transfer. Here are some key ways in which jitter can impact network performance:
1. Voice and Video Quality: Jitter can cause disruptions in real-time communication applications such as voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing. When packets arrive out of order or with varying delays, it leads to distorted audio, dropped calls, and choppy video streams. Users may experience difficulty in understanding conversations or face interruptions during critical discussions.
2. Delay and Latency: Excessive jitter contributes to increased delay and latency in network transmissions. As packets are delayed or arrive at irregular intervals, it leads to a lag in data delivery. This delay can affect various applications, such as online gaming, where real-time responsiveness is crucial. High levels of jitter can result in delayed game actions, adversely impacting the gaming experience.
3. Data Transfer Speed: Jitter can also affect data transfer speeds, particularly when transferring large files or streaming media. Inconsistent packet arrival times can cause retransmissions and reduced throughput. Users may experience slower download or upload speeds, leading to frustration and longer wait times for data-intensive tasks.
4. Application Performance: Jitter can disrupt the performance of latency-sensitive applications. For example, in financial transactions or trading systems, where split-second timing is critical, even slight delays caused by jitter can result in missed opportunities or inaccurate data processing. Similarly, in online collaboration tools or cloud-based applications, increased jitter can lead to reduced productivity and hinder efficient teamwork.
5. User Experience: Ultimately, the impact of jitter on network quality translates into a poor user experience. Users may perceive the network as unreliable, leading to frustration and dissatisfaction. Whether it’s dropped calls, lagging video streams, or slow data transfers, jitter affects the overall quality and usability of network services, diminishing user satisfaction and productivity.
The Importance of Jitter Testing
1. Network Performance Evaluation: Jitter testing provides valuable insights into the performance of a network. By measuring jitter levels, administrators can assess the quality and stability of the network’s data transmission. It helps identify areas of improvement and potential bottlenecks that may be causing excessive jitter. With this information, network administrators can make informed decisions to enhance network performance.
2. Troubleshooting and Issue Diagnosis: Jitter testing serves as a diagnostic tool to identify the root causes of network issues. When users experience disruptions or poor performance, jitter testing helps pinpoint whether excessive jitter is the underlying problem. By isolating and analyzing the jitter patterns, network administrators can identify specific devices, network segments, or configurations that contribute to jitter and take corrective actions accordingly.
3. Network Optimization: Jitter testing provides critical data for optimizing network configurations. By conducting tests under various conditions, administrators can identify the optimal network settings that minimize jitter and enhance overall performance. This may involve adjusting Quality of Service (QoS) settings, optimizing network traffic prioritization, or upgrading network hardware to ensure smoother packet delivery and reduced jitter levels.
4. Quality of Service (QoS) Management: Jitter testing is particularly important for managing QoS in networks. Different types of network traffic, such as voice, video, or data, require different levels of prioritization to maintain their quality. By measuring jitter, administrators can determine whether the network is meeting the required QoS parameters for different applications. Adjustments can be made to QoS policies and configurations based on the jitter test results, ensuring a consistent and satisfactory user experience for critical services.
5. Validation of Network Changes: When implementing changes or upgrades to the network infrastructure, jitter testing helps validate the impact of these changes. By comparing pre- and post-change jitter measurements, administrators can ensure that the network modifications have resulted in improved performance. It provides a quantitative assessment of the effectiveness of network enhancements and helps justify investments in infrastructure upgrades.
6. Proactive Network Monitoring: Regular jitter testing allows for proactive network monitoring. By establishing baseline jitter levels, administrators can set thresholds and receive alerts when jitter exceeds acceptable limits. This enables them to detect potential network issues before they impact user experience or cause disruptions. Proactive monitoring helps ensure a stable and reliable network, reducing downtime and minimizing the negative effects of excessive jitter.
Tips for Conducting Jitter Tests
Here are some key tips to consider when conducting jitter tests:
1. Select appropriate testing tools: Choose reliable network monitoring tools that offer jitter testing capabilities. There are various commercial and open-source tools available that can accurately measure and analyze network jitter like Testmyinternetspeed.org.
2. Test under different conditions: Perform jitter tests under various network conditions, including peak hours, high traffic, and normal usage periods. This helps identify potential issues and variations in network performance.
3. Analyze results and take action: Once the jitter test is complete, analyze the results and look for patterns or trends. If excessive jitter is observed, investigate the possible causes and take corrective measures, such as adjusting network settings or upgrading network infrastructure.
4. Regularly monitor and retest: Network conditions can change over time, so it’s important to conduct periodic jitter tests to ensure ongoing network optimization. Regular monitoring helps detect and address any new or recurring issues promptly
Conclusion
Jitter testing is an essential component of network performance evaluation. By understanding the concept of jitter, its impact on network quality, and the importance of conducting jitter tests, network administrators can proactively manage and optimize network performance. By employing the right tools and following best practices, organizations can ensure a stable and reliable network, enhancing user experiences and enabling seamless communication and data transfer.